Effective Exercises for Sleep Apnea: A Pulmonologist's Guide
Sleep apnea, particularly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), is a condition where the airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing breathing interruptions and potentially serious health complications. While Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy and other medical treatments are common, specific exercises targeting the muscles of the mouth and throat can also be beneficial in managing and reducing symptoms of sleep apnea.
Understanding the Benefits of Sleep Apnea Exercises
These exercises, often referred to as oropharyngeal or myofunctional therapy, aim to strengthen the muscles around the airway. By doing so, they help keep the airway open during sleep, reducing apneic episodes and improving overall sleep quality. Here are some effective exercises recommended by sleep specialists:
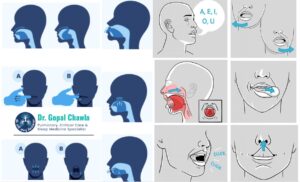
1. Tongue Slide
Purpose: Strengthens tongue muscles to prevent airway collapse.
How to Perform:
1. Place the tip of your tongue against the back of your upper front teeth.
2. Slide your tongue backward along the roof of your mouth.
3. Repeat this movement for 3 minutes daily.
2. Soft Palate Blowing
Purpose: Strengthens the soft palate and throat muscles.
How to Perform:
1. Inhale deeply through your nose.
2. Close your mouth and puff out your cheeks.
3. Press your cheeks gently while keeping your lips sealed.
4. Hold for 10 seconds and repeat 10 times.
3. Throat Tiger Yell
Purpose: Strengthens throat and tongue muscles.
How to Perform:
1. Open your mouth wide as if you are about to roar, but do not make a sound.
2. Stick your tongue out as far as possible.
3. Try to touch your chin with your tongue.
4. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times.
4. Singing Exercises
Purpose: Strengthens the soft palate and upper throat muscles.
How to Perform:
1. Sing various vowel sounds (A, E, I, O, U) loudly and clearly.
2. Focus on controlling your pitch and volume.
3. Practice for 20-30 minutes daily.
5. Jaw Tension Release
Purpose: Relieves jaw tension and strengthens jaw muscles.
How to Perform:
1. Close your mouth and relax your tongue.
2. Open your mouth as wide as possible without causing pain.
3. Hold for 10 seconds, then relax.
4. Repeat 10 times.
6. Straw Exercise
Purpose: Strengthens throat muscles and improves breathing control.
How to Perform:
1. Fill a glass with water and use a straw to suck up the water.
2. Hold the water in the straw by sucking gently.
3. Transfer the water to another glass without spilling.
4. Repeat until you tire.
7. Fish Face
Purpose: Strengthens cheek and jaw muscles.
How to Perform:
1. Suck in your cheeks to make a fish face.
2. Hold for 10 seconds and then relax.
3. Repeat 10 times.
8. Neck Exercise
Purpose: Strengthens neck muscles, improves alignment, potentially enhances airflow, and lessens sleep apnea symptoms.
How to Perform:
1. Sit or stand straight.
2. Slowly tilt your head to the right, bringing your right ear close to your right shoulder.
3. Hold for 10-15 seconds, feeling a light stretch on the left side of your neck.
4. Repeat on the opposite side.
5. Perform this stretch 3-5 times on each side.
9. Mouth Exercise
Purpose: Improves muscle tone in the lips and jaw.
How to Perform:
1. Close your mouth and squeeze your lips tightly together.
2. Hold briefly and then release.
3. Move your jaw forward and hold for a few seconds.
4. Make a clicking noise by pressing your tongue inside your bottom teeth.
5. Repeat multiple times.
10. Oropharyngeal Exercises
Purpose: Strengthens the soft palate and muscles in the back of the throat.
How to Perform:
1. Open your mouth widely.
2. Stick your tongue out as far as possible.
3. Say “Ahhh” for as long as you can.
4. Repeat daily to improve muscle tone and control in the upper airway.
Additional Tips for Managing Sleep Apnea
While exercises can help, it's important to complement them with other lifestyle changes and treatments:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the severity of OSA.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your side rather than your back can prevent airway obstruction.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Both can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms by relaxing the throat muscles.
It's crucial to emphasize that while these exercises can provide relief, they are most effective when combined with comprehensive sleep apnea treatment plans, including the use of CPAP therapy. A CPAP machine maintains continuous airflow, preventing the airway from collapsing during sleep. Additionally, undergoing a professional sleep study is essential to accurately diagnose the severity of sleep apnea and tailor an appropriate treatment plan. Always consult with a pulmonologist or sleep specialist to ensure you receive the most effective care for your condition.

