Pneumonia
Lobar pneumonia and bronchopneumonia are two different types of bacterial pneumonia, which is an infection of the lungs caused by various bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus, among others.
1. Lobar Pneumonia:
Lobar pneumonia, also known as focal pneumonia, is a type of pneumonia that primarily affects one or more lobes of a lung. A lobe is a specific section of the lung, and when this type of pneumonia occurs, it involves the entire lobe(s). The infection typically starts in a single lobe and may spread to other adjacent lobes.
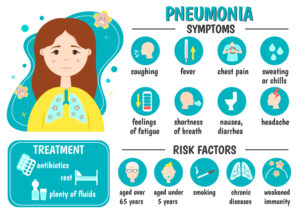
Symptoms of lobar pneumonia include:
- High fever
- Chills
- Productive cough with yellow or greenish mucus
- Chest pain
- Rapid breathing (tachypnea)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and weakness
Lobar pneumonia often presents as a well-defined, consolidated area on chest X-rays, representing the affected lobe(s) of the lung.
2. Bronchopneumonia:
Bronchopneumonia, also known as lobular pneumonia or bronchial pneumonia, is a type of pneumonia that affects multiple small areas in both lungs. It is characterized by patches of inflammation and infection scattered throughout the bronchioles (small airways) and surrounding alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs.

Symptoms of bronchopneumonia include:
- Mild to high fever
- Cough, sometimes with blood-tinged mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- General malaise and fatigue
On chest X-rays, bronchopneumonia appears as diffuse, patchy infiltrates in various parts of the lungs.
While both lobar pneumonia and bronchopneumonia are caused by bacterial infections, their patterns of involvement in the lungs differ. Lobar pneumonia affects entire lobes, while bronchopneumonia involves multiple smaller areas scattered throughout the lung tissue.
The treatment for both types of pneumonia typically involves antibiotics to target the underlying bacterial infection, along with supportive measures to manage symptoms and improve lung function. It is essential to seek prompt medical attention if pneumonia is suspected to prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment.

